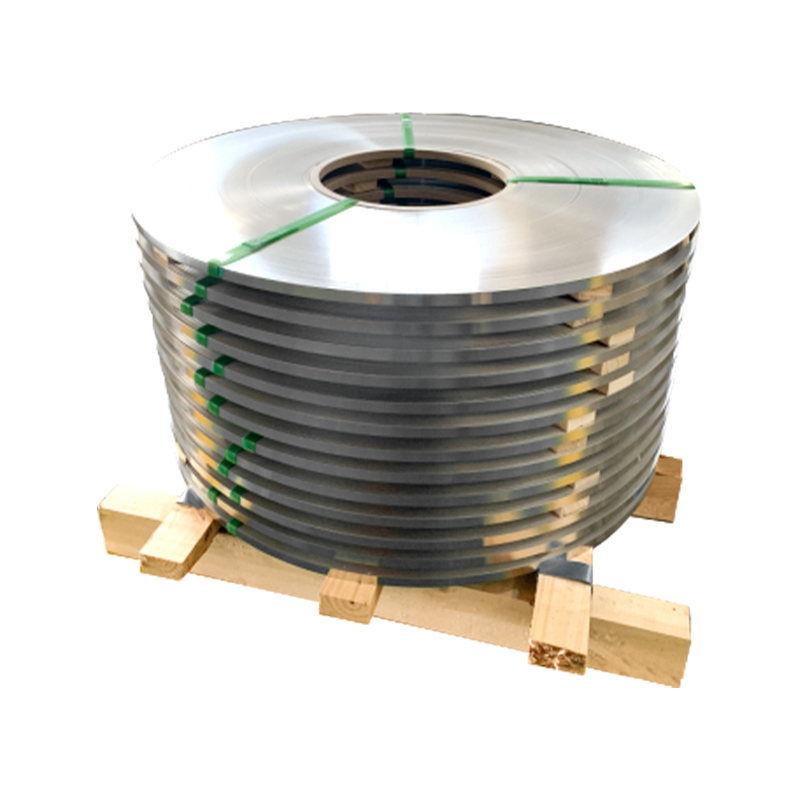
Stainless steel has become one of the most widely used metals in industrial, construction, and consumer applications due to its strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Among the various grades of stainless steel, 201 stainless steel has gained popularity as a cost-effective alternative to higher-end grades such as 304 or 316. Manufactured primarily from iron, chromium, and nickel, with added manganese and nitrogen, 201 stainless steel strips provide a balance of mechanical strength and aesthetic appeal. However, questions often arise regarding their resistance to rust, corrosion, and high-temperature environments, especially when used in challenging applications.
Chemical Composition and Its Role in Corrosion Resistance
201 stainless steel is part of the austenitic stainless steel family, which is characterized by a face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure that enhances ductility and toughness. The standard chemical composition includes:
- Chromium (16–18%): Chromium forms a passive oxide layer on the surface, which protects the steel from oxidation and rust.
- Nickel (3.5–5.5%): Nickel stabilizes the austenitic structure and improves ductility and corrosion resistance.
- Manganese (5.5–7.5%): Manganese partially replaces nickel to reduce costs while maintaining corrosion resistance.
- Carbon (≤0.15%): Low carbon content minimizes carbide precipitation, reducing the risk of intergranular corrosion.
- Nitrogen (0.08–0.25%): Enhances strength and helps resist localized corrosion.
The combination of chromium, nickel, and manganese allows 201 stainless steel to resist mild oxidation and some corrosive environments. However, because it has lower nickel content than 304 stainless steel, its corrosion resistance is comparatively reduced in harsh conditions, especially in chloride-rich or acidic environments.
Resistance to Rust and Oxidation
Rust formation, primarily caused by the reaction of iron with oxygen and moisture, is a key concern in stainless steel applications.
201 stainless steel performance against rust:
- Mild environments: In indoor applications or areas with low humidity, 201 stainless steel strips exhibit good resistance to rust due to the protective chromium oxide layer.
- Moist or humid conditions: Prolonged exposure to moisture, particularly in coastal regions with high salt content, can lead to surface oxidation and rust spots.
- Preventive measures: Applying surface coatings, such as passivation, electro-polishing, or protective paint, can significantly improve rust resistance.
While 201 stainless steel can maintain its appearance in many indoor applications, it is less suitable for marine environments or locations with heavy exposure to chlorides compared to higher nickel content grades like 304 or 316 stainless steel.
Corrosion Resistance in Different Environments
Corrosion resistance is the ability of stainless steel to withstand chemical or electrochemical attack, including oxidation, pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking.
Key observations regarding 201 stainless steel strips:
-
Acidic environments:
- 201 stainless steel has moderate resistance to weak acids like acetic or citric acid.
- Strong acids, such as hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, can rapidly degrade the surface if exposure is prolonged.
-
Alkaline environments:
- Generally resistant to mild alkaline solutions.
- Highly concentrated caustic substances at elevated temperatures may cause localized corrosion.
-
Chloride-rich environments:
- Chloride ions, commonly found in seawater and de-icing salts, can penetrate the protective oxide layer and cause pitting corrosion.
- This makes 201 stainless steel less suitable for marine or coastal applications without additional protective measures.
-
Oxidizing vs. reducing conditions:
- The steel performs better in oxidizing environments, where the passive layer is stable.
- Reducing environments, such as sulfide-rich atmospheres, may lead to surface degradation over time.
Practical takeaway: For indoor appliances, kitchenware, and light-duty structural components, 201 stainless steel offers sufficient corrosion resistance. For harsh industrial, chemical, or marine applications, higher-grade stainless steels (304 or 316) are recommended.
High-Temperature Performance
The performance of 201 stainless steel strips at elevated temperatures is crucial for applications in heat exchangers, automotive components, and industrial machinery.
Temperature limitations and behavior:
- Continuous service: 201 stainless steel can withstand temperatures up to 425°C (797°F) for prolonged periods without significant loss of mechanical properties.
- Intermittent exposure: Short-term exposure to up to 870°C (1598°F) is possible, although oxidation may occur on the surface.
- Scaling and oxidation: Above 500°C, the steel may develop scaling or discoloration due to the growth of iron oxides.
Comparison with other stainless steels:
- 304 and 316 stainless steels perform better at high temperatures due to higher nickel and molybdenum content.
- 201 stainless steel is suitable for moderate heat applications, such as kitchen equipment, automotive trim, and indoor heating components, but not for extreme high-temperature industrial furnaces.
Mechanical Strength and Structural Integrity
Corrosion and temperature resistance are closely linked to mechanical performance. Stainless steel strips must maintain strength, ductility, and toughness under service conditions.
201 stainless steel characteristics:
- Tensile strength: Approximately 520–750 MPa, depending on processing and temper.
- Yield strength: Around 205–450 MPa.
- Ductility: Moderate, allowing bending, stamping, and forming without cracking.
- Work-hardening ability: High, enabling cold forming for strips and sheets.
These properties make 201 stainless steel strips suitable for fabrication into household appliances, automotive components, and decorative items, where moderate corrosion and heat resistance are adequate.
Surface Treatments to Enhance Resistance
To improve rust and corrosion resistance, manufacturers often apply surface treatments to 201 stainless steel strips:
- Polishing: Smooths the surface, reduces crevices, and minimizes areas for corrosion initiation.
- Passivation: Treating the steel with nitric or citric acid strengthens the chromium oxide layer.
- Electroplating or coating: Applying protective layers, such as nickel, chrome, or powder coatings, improves aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance.
- Lacquer or film application: Transparent coatings can protect against environmental moisture and reduce oxidation.
These treatments extend the lifespan of 201 stainless steel strips in applications that might otherwise cause surface rust or degradation.
Applications of 201 Stainless Steel Strips Based on Environmental Resistance
Given its properties, 201 stainless steel strips are widely used in applications with moderate corrosion and temperature demands:
- Home appliances: Refrigerator panels, washing machine parts, microwave components.
- Automotive trim: Decorative strips, interior panels, exhaust trim (moderate heat areas).
- Construction: Decorative architectural elements, handrails, and light-duty metal frameworks.
- Kitchenware: Cutlery, food trays, and light-duty cookware.
- Furniture: Metal furniture accents and fittings.
However, for marine hardware, chemical processing equipment, or high-temperature industrial components, 201 stainless steel is generally avoided due to potential corrosion and oxidation under extreme conditions.
Comparison with Other Stainless Steel Grades
| Property | 201 Stainless Steel | 304 Stainless Steel | 316 Stainless Steel |
| Nickel content | 3.5–5.5% | 8–10.5% | 10–14% |
| Corrosion resistance | Moderate | High | Very high (especially in chlorides) |
| Heat resistance | Moderate | High | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher | Highest |
| Best use | Indoor, moderate environments | Kitchenware, automotive, light outdoor | Marine, chemical, extreme environments |
The comparison highlights the trade-off between cost and performance, with 201 stainless steel offering an affordable option where extreme corrosion or high-temperature resistance is not required.
Maintenance Recommendations
Even though 201 stainless steel strips are reasonably resistant, proper care ensures longevity:
- Avoid prolonged exposure to salty or acidic environments.
- Clean regularly with mild detergents and soft cloths to remove contaminants.
- Avoid abrasive cleaning methods that can damage the protective oxide layer.
- Apply protective coatings or polish periodically for outdoor or semi-outdoor applications.
These practices help prevent premature rusting and maintain both aesthetic and structural integrity.
Conclusion
201 stainless steel strips offer moderate resistance to rust, corrosion, and high temperatures, making them suitable for a wide range of indoor and decorative applications. Their cost-effectiveness, combined with good mechanical properties, makes them popular for appliances, automotive trim, kitchenware, and architectural elements.
However, their lower nickel content compared to 304 or 316 stainless steel means that they are less ideal for highly corrosive, marine, or extreme high-temperature environments. With proper surface treatment, maintenance, and thoughtful application, 201 stainless steel strips provide a practical balance of performance, durability, and affordability for everyday use.
By understanding the limitations and advantages of 201 stainless steel, engineers, designers, and manufacturers can make informed decisions about where and how to use this material efficiently.

 English
English русский
русский